A very illustrative video to prevent Repetitive Strain Injuries (RSI) when using computer, Also Parents please aware of the postural deformities, Muscle weakness, Eye problems, laziness, stress, depression, generalized malaise which occurs to your young ones when they are free to use computers for playing games or web search.. Please be a mentor for their physical and psychological well being instead of jargon computer games.. These physical games enhances they mood, sweats out their energy so that they tend to eat more healthily which in turn reduces childhood obesity (infantile obesity, teenage obesity).
Most Common For Computer Users !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
Repetitive strain injury (RSI) (also known as repetitive stress injury, repetitive motion injuries, repetitive motion disorder (RMD), cumulative trauma disorder (CT), occupational overuse syndrome, overuse syndrome, regional musculoskeletal disorder) is an injury of the musculoskeletal and nervous systems that may be caused by repetitive tasks, forceful exertions, vibrations, mechanical compression (pressing against hard surfaces), or sustained or awkward positions. Different sections of this article present contrasting perspectives regarding the causes of RSI.
Types of RSIs that affect computer users may include non-specific arm pain or work related upper limb disorder (WRULD). Conditions such as RSI tend to be associated with both physical and psychosocial stressors.
Other typical habits that some sources believe lead to RSI:[citation needed]
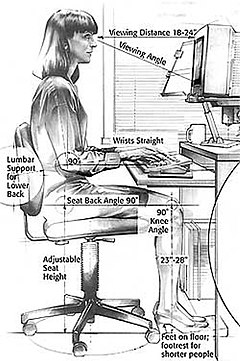
The most often prescribed treatments for repetitive strain injuries are rest, exercise, braces and massage. A variety of medical products also are available to augment these therapies. Since the computer workstation is frequently blamed for RSIs, particularly of the hand and wrist, ergonomic adjustments of the workstation are often recommended.
KOUSHIK's Health line
Most Common For Computer Users !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
Repetitive strain injury (RSI) (also known as repetitive stress injury, repetitive motion injuries, repetitive motion disorder (RMD), cumulative trauma disorder (CT), occupational overuse syndrome, overuse syndrome, regional musculoskeletal disorder) is an injury of the musculoskeletal and nervous systems that may be caused by repetitive tasks, forceful exertions, vibrations, mechanical compression (pressing against hard surfaces), or sustained or awkward positions. Different sections of this article present contrasting perspectives regarding the causes of RSI.
Types of RSIs that affect computer users may include non-specific arm pain or work related upper limb disorder (WRULD). Conditions such as RSI tend to be associated with both physical and psychosocial stressors.
Causes
RSI is believed by many to be caused due to lifestyle without ergonomic care[citation needed], E.g. While working in front of computers, driving, traveling etc. Simple reasons like 'Using a blunt knife for everyday chopping of vegetables', may cause RSI.Other typical habits that some sources believe lead to RSI:[citation needed]
- Reading or doing tasks for extended periods of time while looking down.
- Sleeping on an inadequate bed/mattress or sitting in a bad armchair and/or in an uncomfortable position.
- Carrying heavy items.
- Holding one's phone between neck and shoulder.
- Watching TV in incorrect position e.g. Too much to the left/right.
- Sleeping with head forward, while traveling.
- Prolonged use of the hands, wrists, back, neck, etc.
Treatment
On their own, most RSIs will resolve spontaneously provided the area is first given enough rest when the RSI first begins. However, without such care, some RSIs have been known to persist for years, or have needed to be cured with surgery.The most often prescribed treatments for repetitive strain injuries are rest, exercise, braces and massage. A variety of medical products also are available to augment these therapies. Since the computer workstation is frequently blamed for RSIs, particularly of the hand and wrist, ergonomic adjustments of the workstation are often recommended.
Ergonomics
Modifications of posture and arm use (ergonomics) are often recommended.
Exercise
Exercise decreases the risk of developing RSI.- Doctors sometimes recommend that RSI sufferers engage in specific strengthening exercises, for example to improve posture.
- In light of the fact that a lifestyle that involves sitting at a computer for extended periods of time increases the probability that an individual will develop excessive kyphosis, theoretically the same exercises that are prescribed for thoracic outlet syndrome or kyphotic postural correction would benefit an RSI sufferer.
- Some sources recommend motoric exercises and ergo-aerobics to decrease chances of strain injury. Ergo-aerobics target touch typists and people who often use computer keyboard.
Adaptive hardware
Adaptive technology ranging from special keyboards, mouse replacements to pen tablet interfaces might help improve comfort.Mouse
Switching to a much more ergonomic mouse, such as a roller mouse, vertical mouse or joystick, or switching from using a mouse to a stylus pen with graphic tablet may provide relief, but in chronic RSI they may result only in moving the problem to another area. Using a graphic tablet for general pointing, clicking, and dragging (i.e. not drawing) may take some time to get used to as well. Switching to a trackpad or pointing stick, which requires no gripping or tensing of the muscles in the arms may help as well. Inertial mice (which do not require a surface to operate) might offer an alternative where the user's arm is in a less stressful thumbs up position rather than rotated to thumb inward when holding a normal mouse. Also, since they do not need a surface to operate ("air mice" function by small, forceless, wrist rotations), the wrist and arm can be supported by the desktop.Keyboards and keyboard alternatives
Exotic keyboards by manufacturers such as Datahand, OrbiTouch, Maltron and Kinesis are available. Also one can use digital pens to avoid the strain coming from typing itself. Other solutions move the mode of input from one's hands entirely. These include the use of voice recognition software or pedals designed for ergonomics and gaming to supplant normal keyboard input.Adaptive software
Main article: List of Repetitive Strain Injury software
There are several kinds of software designed to help in Repetitive Strain Injury. Among them, there are speech recognition software, and break timers. Break timers software reminds the user to pause frequently and perform exercises while working behind a computer. There is also automated mouse-clicking software that has been developed, which can automate repetitive tasks in games and applications.KOUSHIK's Health line